When a partition, especially the C: drive is getting full in a Windows Server, the most effective solution is to extend the partition by reallocating free space from another partition on the same disk. As with previous versions, the native Disk Management tool in Windows includes an "Extend Volume" option. However, many users have reported that they cannot extend volume in Windows Server 2022/2025 because "Extend Volume" is grayed out. This article explains why Disk Management cannot extend partitions in Server 2022/2025 and provides simple solutions to resolve this issue.

Reasons why you cannot extend volume in Windows Server 2022
There are 4 common reasons why Disk Management can't extend volume in Windows Server 2022/2025:
- The partition to be extended is not formatted with NTFS file system.
- There's no adjacent unallocated space on the right.
- When you delete a partition to extend another one, the type of them are different.
- You try to extend a 2TB partition on a MBR disk.
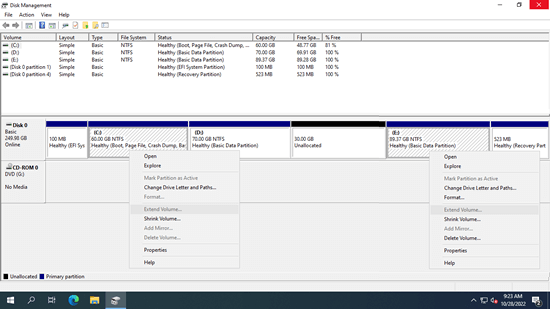
I'll explain the reasons more clearly one by one. To better understand, you may press Windows + X to open your own Disk Management.
Reason 1: Partition is not NTFS
This is easy to understand. NTFS and FAT32 are common partitions in Windows computers, but only NTFS partition can be shrunk and extended by Disk Management (and another diskpart command tool). If the partition to be extended is not formatted with NTFS file system, "Extend Volume" is grayed out with no doubt.
Reason 2: No adjacent unallocated space on the right
This is the most common reason why you can't extend volume in Windows Server 2022/2025 via Disk Management or diskpart command. There are 3 points you should know:
- There should be unallocated space on the same disk. Unlike free space in a partition, unallocated space is not allocated to any partition. To get this kind of space, you may either shrink or delete a partition.
- This unallocated space must be adjacent to the NTFS partition that you want to extend.
- This unallocated space must be on the right of the partition to be extended.
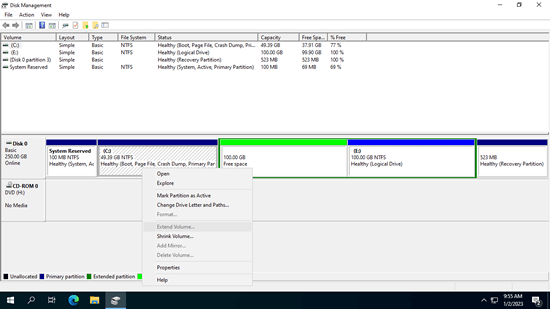
When you shrink a volume, such as the D: drive, using Disk Management (or the diskpart command), unallocated space is created on the right of the shrunken volume. This space is nonadjacent to the C: drive and is positioned on the left of the E: drive. As a result, when you right-click either of these two partitions in Disk Management, the "Extend Volume" option is disabled.
Reason 3: Different partition type
Because some users cannot extend the C: drive in Server 2022 after shrinking the D: drive, they want to know what happens if the D: drive is deleted. First, it is important to understand that a disk can be initialized as either MBR or GPT. On a GPT disk, all partitions are created as primary. However, on an MBR disk, there can be a mix of primary and logical drives. When deleting a partition to extend the left contiguous one, both partitions must be the same type - either primary or logical drives.
C drive is primary partition in almost all computers. That means, if you want to delete D to extend C, D drive must be primary partition, too. Otherwise, "Extend Volume" is still grayed out after deleting D.
Caution: do not delete this partition if you installed programs or there are Windows services running from it.
Reason 4: 2TB restriction on MBR disk
Another limitation of MBR disks is that they can only handle a maximum partition size of 2TB. If a single partition is already 2TB, or if the total capacity of all partitions on the disk reaches 2TB, you cannot extend any partition to be larger—even if there is adjacent unallocated space on the right side.
What to do when you cannot extend partition in Server 2022
When you are unable to extend volume in Windows Server 2022/2025 with inbuilt tools, NIUBI Partition Editor can solve this problem no matter which reason it is. However, the methods are different. Open your own Disk Management and find out associated reason and follow corresponding method.
Methods when you cannot extend volume in Windows Server 2022/2025:
- Shrink adjacent partition to make unallocated space on either side.
- Move nonadjacent unallocated space to be adjacent on either side.
- Convert MBR disk to GPT before extending partition.
Method 1: Shrink partition to make unallocated space
When there's free space in another partition on the same disk, run NIUBI Partition Editor to shrink partition, then part of free space will be changed to unallocated. All files in that partition keeps intact. Better than Windows inbuilt tools, NIUBI can make unallocated space on either left or right when shrinking a partition.
Download NIUBI Partition Editor and follow the steps in the video:
Method 2: Move unallocated space to be adjacent
If you've shrunk D drive and made unallocated space with Disk Management or diskpart command, as I explained above, this unallocated space can't be combined to other partition without third-party software.
What to do when you cannot extend volume in Server 2022/2025 after shrinking partition:
- Right click D: drive in NIUBI Partition Editor and select "Resize/Move Volume", drag the the middle of D drive to the right in the pop-up window, then unallocated space will be moved to the left at the same time.
- Right click C: drive and run "Resize/Move Volume", drag the right border to the right to combine this unallocated space.
- Click "Apply" on top left to take effect.
If you want to extend E drive after shrinking D, you can accomplish without moving unallocated space. To do this, right click E: drive and click "Resize/Move Volume", drag the left border to the left in the pop-up window.
Watch the video how to move partition D to extend C drive:
Method 3: Convert MBR to GPT
You'll overcome the 2TB restriction and extend partition much larger after converting MBR to GPT. Follow the steps in the video to convert MBR to GPT in Server 2022:
In summary, if you cannot extend a partition in Windows Server 2022/2025, open Disk Management to identify the associated reason and then follow the corresponding method outlined above. In addition to shrinking, moving, extending, and converting disk partitions, NIUBI Partition Editor enables you to perform many other disk partition management operations for Windows Server 2022/2025 and previous versions, including Server 2019, 2016, 2012, 2008, and 2003.